
CHEBI:48928
| Name | 6-phospho-D-gluconic acid | 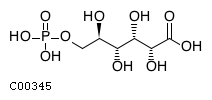 Download: mol | sdf |
| Synonyms | 06-o-phosphonato-d-gluconate; 6-phospho-d-gluconate; 6-phosphogluconate; 6-phosphogluconic acid; | |
| Definition | A gluconic acid phosphate having the phosphate group at the 6-position. It is an intermediate in the pentose phosphate pathway. | |
| Molecular Weight (Exact mass) | 276.1352 (276.0246) | |
| Molecular Formula | C6H13O10P | |
| SMILES | O[C@H](COP(O)(O)=O)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@@H](O)C(O)=O | |
| InChI | InChI=1S/C6H13O10P/c7-2(1-16-17(13,14)15)3(8)4(9)5(10)6(11)12/h2-5,7-10H,1H2,(H,11,12)(H2,13,14,15)/t2-,3-,4+,5-/m1/s1 | |
| InChI Key | BIRSGZKFKXLSJQ-SQOUGZDYSA-N | |
| Crosslinking annotations | KEGG:C00345 | 3DMET:B01221 | ChEBI:48928 | ChEMBL:CHEMBL1230513 | KNApSAcK:C00007481 | NIKKAJI:J1.343.743B | PDB-CCD:6PG | PubChem:3638 | |
| Pathway ID | Pathway Name | Pathway Description (KEGG) |
| map00030 | Pentose phosphate pathway | The pentose phosphate pathway is a process of glucose turnover that produces NADPH as reducing equivalents and pentoses as essential parts of nucleotides. There are two different phases in the pathway. One is irreversible oxidative phase in which glucose-6P is converted to ribulose-5P by oxidative decarboxylation, and NADPH is generated [MD:M00006]. The other is reversible non-oxidative phase in which phosphorylated sugars are interconverted to generate xylulose-5P, ribulose-5P, and ribose-5P [MD:M00007]. Phosphoribosyl pyrophosphate (PRPP) formed from ribose-5P [MD:M00005] is an activated compound used in the biosynthesis of histidine and purine/pyrimidine nucleotides. This pathway map also shows the Entner-Doudoroff pathway where 6-P-gluconate is dehydrated and then cleaved into pyruvate and glyceraldehyde-3P [MD:M00008]. |
| map01100 | Metabolic pathways | NA |
| map01110 | Biosynthesis of secondary metabolites | NA |
| map01120 | Microbial metabolism in diverse environments | NA |
| map01130 | Biosynthesis of antibiotics | NA |
| map01200 | Carbon metabolism | Carbon metabolism is the most basic aspect of life. This map presents an overall view of central carbon metabolism, where the number of carbons is shown for each compound denoted by a circle, excluding a cofactor (CoA, CoM, THF, or THMPT) that is replaced by an asterisk. The map contains carbon utilization pathways of glycolysis (map00010), pentose phosphate pathway (map00030), and citrate cycle (map00020), and six known carbon fixation pathways (map00710 and map00720) as well as some pathways of methane metabolism (map00680). The six carbon fixation pathways are: (1) reductive pentose phosphate cycle (Calvin cycle) in plants and cyanobacteria that perform oxygenic photosynthesis, (2) reductive citrate cycle in photosynthetic green sulfur bacteria and some chemolithoautotrophs, (3) 3-hydroxypropionate bi-cycle in photosynthetic green nonsulfur bacteria, two variants of 4-hydroxybutyrate pathways in Crenarchaeota called (4) hydroxypropionate-hydroxybutyrate cycle and (5) dicarboxylate-hydroxybutyrate cycle, and (6) reductive acetyl-CoA pathway in methanogenic bacteria. |

